

Disha Gupta


Large organizations understand the need for a dedicated L&D strategy that develops leaders from within, upskills employees to become influential team members, and utilizes various learning methods and training techniques to drive skill acquisition.
In this article, we explore the various training methods, including traditional instruction-led learning, eLearning experiences, and hands-on training, to identify the more effective employee training methods for corporate learning.
By uncovering each method’s strengths, limitations, and applications, we aim to provide insights that empower organizations to design training programs that foster continuous learning, skill enhancement, and adaptability in an ever-changing professional landscape.
Employee training methods refer to the various approaches and techniques used to educate and develop employees’ skills, knowledge, and competencies. These methods are designed to enhance employees’ job performance, job satisfaction, and overall effectiveness within an organization.
Employee training methods encompass a wide range of strategies, from traditional classroom-based training to modern technology-driven approaches. The choice of training methods depends on factors such as the nature of the content, the learning objectives, the target audience, available resources, and the organization’s goals.
Here’s a list of eigtheen common employee training methods found in the workplace:
eLearning has become one of the most recognized employee training methods, accelerated by COVID-19 and the move to hybrid and remote work. eLearning enables employees to learn via a web browser and provides learning that adapts to different learning styles and needs.
Modern organizations leverage corporate learning management systems (LMS) and instructional design software to create training courses, manage learning content, distribute training, and assess performance.
Advantages of eLearning
Disadvantages of eLearning
On-the-job training (also known as hands-on training) enables employees’ active participation by allowing them to learn in the flow of work. The end goal of on-the-job training is faster task mastery or accelerated time-to-proficiency.
Hands-on training embraces the 70-20-10 rule of learning which states:
Advantages of on-the-job training
Disadvantages of on-the-job training
PRO TIP
With Whatfix, your employees can learn in the flow of work via in-app guidance and simulated application environments.
With Whatfix Mirror, quickly create and manage replica versions of your mission-critical applications (like your CRM or ERP) to provide hands-on training to end-users without risking live software usage.
With Whatfix Digital Adoption Platform (DAP), create in-app guided to support your employees within the digital workplace. With Whatfix DAP, use Tours and Task Lists to onboarding new employees and reduce time-to-proficiency on core application, use Flows to drive adoption of advanced workflows or infrequently done tasks, and Smart Tips provide additional context to employees or nudge them to take specific action. Self Help provides employees with an in-app help center that integrates with your LMS, process documentation, SOP, and other knowledge repositories, allowing employees to find answers to process-related questions and technical support without leaving their application.
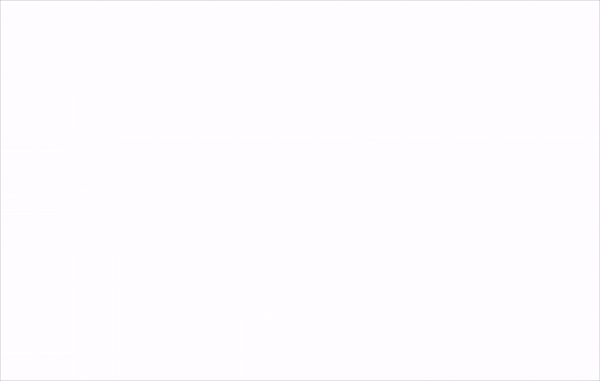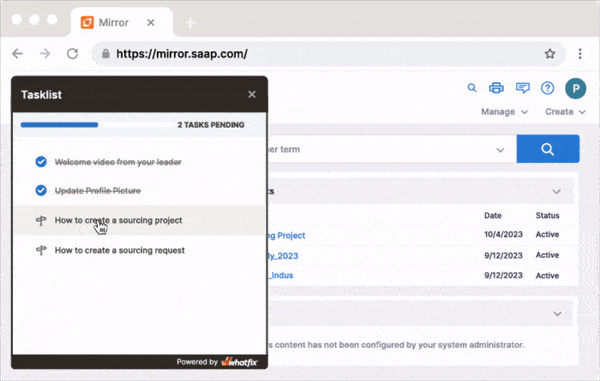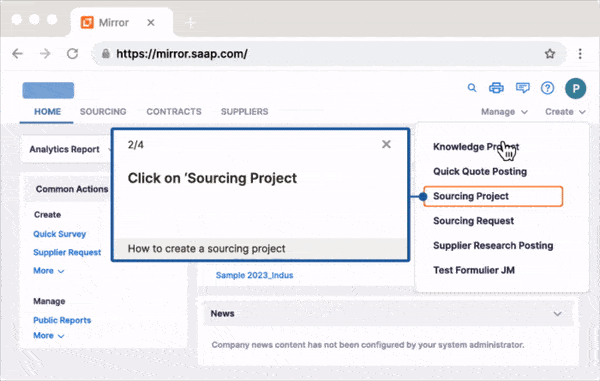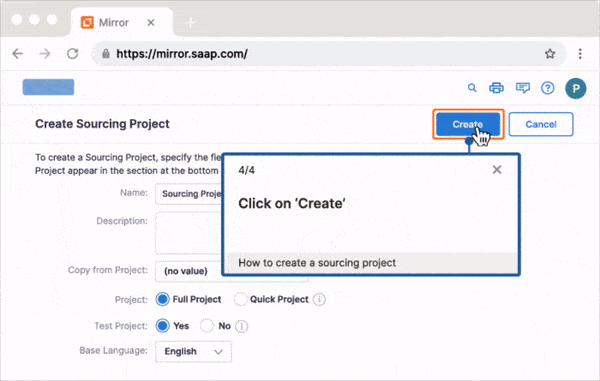
Instructor-led training is one of the most traditional and popular types of employee training techniques. It mimics physical classroom spaces, with an instructor present to lead the training session. This usually occurs using a lecture-style presentation with supporting visual components.
Advantages of instructor-led training
Disadvantages of instructor-led training
This technique is when a learner and an instructor both act out their roles in potential workplace scenarios. This method is most effective for employees whose job roles include direct client or customer interaction, as it gives them some experience in handling difficult situations with customers (like customer service training or call center training.)
Advantages of role playing
Disadvantages of role playing
The coaching method involves an experienced professional—a supervisor, mentor, or veteran employee—who mentors or coaches an employee on specific job tasks and responsibilities. The method can be implemented in person or virtually using coaching software, making it ideal for both in-office and remote workforces.
Advantages of job coaching
Disadvantages of job coaching
Simulation training lays out different scenarios that allow employees to practice tasks that mimic the actual work of their specific job’s role. This is an ideal training method for employees working in high-risk or high-stakes fields such as pilots or doctors. Many times, simulation training is mandated by the state or federal government and it’s called compliance training.
Advantages of simulated training
Disadvantages of simulated training
Collaborative training is a methodology in which employees share their knowledge and expertise, teaching and learning from one another. This technique helps enhance the overall training experience for employees by capitalizing on their skills, ideas, and knowledge.
Advantages of collaborative training
Disadvantages of collaborative training
Video training is one of the most effective team member training methods to engage employees and deliver sophisticated learning experiences at a lower cost than traditional training. Creating training videos for employees enables them to digest information in an easy-to-understand format that is easier to retain, and that employees can go back and watch at any time.
Advantages of video training
Disadvantages of video training
Cross-training involves teaching an employee hired to perform one job function the skills to perform new job functions. This allows them to offer support in the time of need instead of having to outsource work.
Employees find cross-training beneficial for their personal growth. It allows them to learn new skills to enhance their value within the organization or switch to a role that is more aligned with their career aspirations.
Advantages of cross-training
Disadvantages of cross-training
Job shadowing allows employees to follow and observe other professionals working in different job functions to gain insight into their work area. It is also implemented to allow lesser experienced individuals to work alongside experienced professionals to sharpen their skills from those already mastered them.
Advantages of job shadowing
Disadvantages of job shadowing
With the case study method, employees are presented with a real or fictional complex situation to analyze and use as a reference for their solutions. While cases vary in complexity and detail, trainees should be given enough data and information to analyze the situation and devise solutions.
Advantages of case studies
Disadvantages of case studies
Peer-to-peer learning is a mutual learning strategy that involves participants of the same level engaging in collaborative learning. This type of learning allows employees to work through new concepts and share ideas with their peers working on the same project. The opportunity to teach and be taught by one another is an effective way for organizations to grow stronger employees who work together productively.
Advantages of peer-to-peer learning
Disadvantages of peer-to-peer learning
Spaced learning breaks down long employee training programs into several sessions or modules of shorter durations, with spaced intervals in between. Parts of these sessions are reintroduced multiple times over the next few days or weeks for learners to recall information, driving long-term knowledge retention.
Spaced repetition learning is based on research from Hermann Ebbingaus, a 19th-century psychologist, who discovered that information is forgotten over a period of time when no effort is made to repeat it (known as the Forgetting Curve). Later, this was the foundation of the learning curve theory, which states that task master can be represented on a graphic, with mastery happening over time as learners continuously practice a task.
Advantages of spaced learning
Disadvantages of spaced learning
Gamification in training incorporates gaming elements such as points and badges into training courses. By leveraging psychology, gamified training engages learners and makes them more willing to take on repetitive tasks despite the risk of failure. Gamification of training has been shown to increase employee performance and the adoption of new software.
Advantages of gamified training
Disadvantages of gamified training
Mobile learning (or mLearning) refers to online learning via a personal mobile device such as a smartphone, tablet, or laptop. This training method empowers learning on the go, enabling users to access content whenever and wherever they want.
Advantages of mobile learning
Disadvantages of mobile learning
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face learning and eLearning to create a more holistic, effective training system. It leverages the best in-person learning experiences (like social learning and subject-matter-expert-led training lessons) with online learning (via LMS courses, hands-on training experiences, etc.) to provide a comprehensive, multi-method approach to learning and development.
Advantages of blended learning
Disadvantages of blended learning
Microlearning is an approach to learning new knowledge that breaks learning content into small, bite-sized information modules. Smaller learning sessions provide all the information necessary for learners to achieve a specific training objective quickly, making microlearning valuable in business contexts.
Advantages of microlearning
Disadvantages of microlearning
Adaptive learning utilizes AI and big data technology to facilitate individualized learning experiences based on several learner factors and inputs to build contextual paths for employees that drive L&D outcomes.
Courses are adapted based on a learner’s profile and preferences, previous knowledge of a concept, behaviors, and performance. Experiences are adapted by presenting real-time feedback to learners, presenting new pathways that aren’t “pass” or “fail”, and can present contextual tooltips or future resources for learning more. The experience adapts its content, sequence, and assessment based on all previous actions and factors.
Advantages of adaptive learning
Disadvantages of adaptive learning
Here are a few factors to consider while choosing the right training method for your employees.
The learning objectives and content of the training are fundamental in determining the appropriate training methods. Different methods excel at achieving certain types of objectives.
For instance, if the training aims to teach technical skills, hands-on methods such as simulations or on-the-job training might be effective. On the other hand, for theoretical concepts, eLearning or instructor-led sessions work well. The content’s complexity, depth, and practicality influence which method aligns best with the desired learning outcomes.
Understanding the preferences of their learners is vital for L&D managers. People have different learning styles, some respond better to visual content, while others prefer interactive discussions.
Gathering information about how your learners like to learn guides you in selecting a method that resonates with them. Catering to your learners’ preferences enhances engagement, motivation, and the effectiveness of the training.
Consider the logistics of training, including where and when it will take place. If your workforce is geographically dispersed, virtual methods might be more suitable. Accessibility is also crucial—can employees easily access the training content? Ensure that the chosen method aligns with participants’ availability and accommodates their schedules, especially for remote or shift-based workers.
Different training methods come with varying costs in terms of both money and resources. Some methods, like eLearning or mobile learning, might require investments in technology and content development. Others, like instructor-led training, might involve hiring trainers and renting physical spaces. Assess your organization’s budget and resource availability to choose a method that aligns with your financial capabilities.
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements and the ever-growing need for skill agility, the integration of digital adoption platforms (DAPs) marks a transformative shift in the landscape of employee training.
As organizations strive to empower their workforce with the skills and knowledge required to navigate complex digital environments, DAPs emerged as catalysts of success.
With no-code platforms like Whatfix DAP, organizations can create in-app guided training and performance support that overlays employee workflows and tasks. This guidance enables employees to learn in the flow of work, which is more effective than traditional classroom-style learning techniques. According to the 70-20-10 learning model, 70% of all skill acquisition and institutional knowledge comes from hands-on experiences.
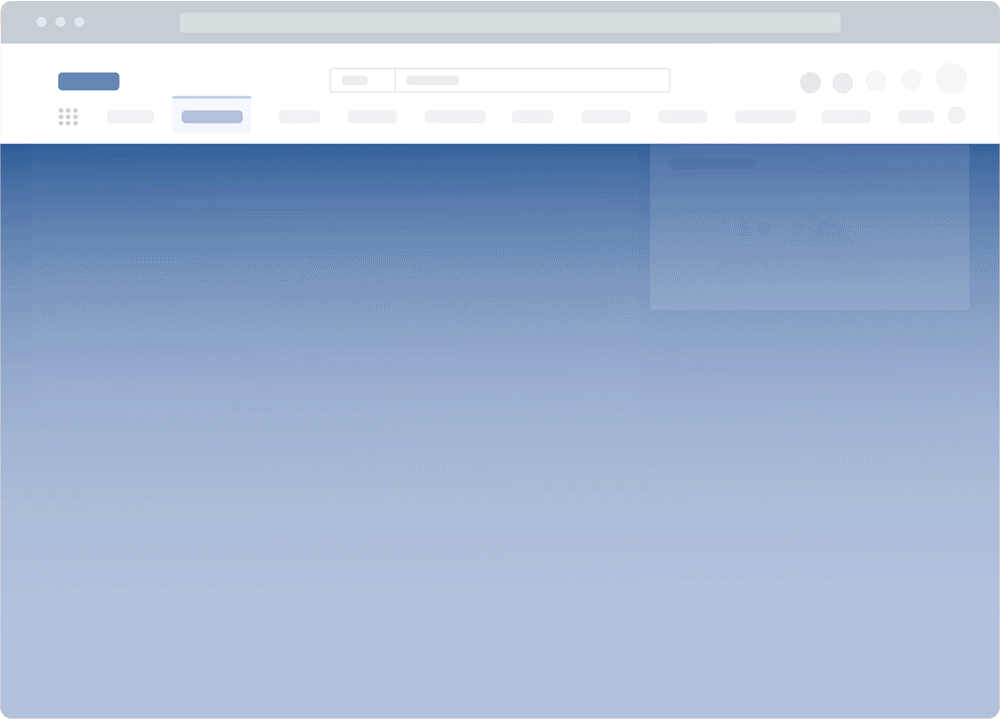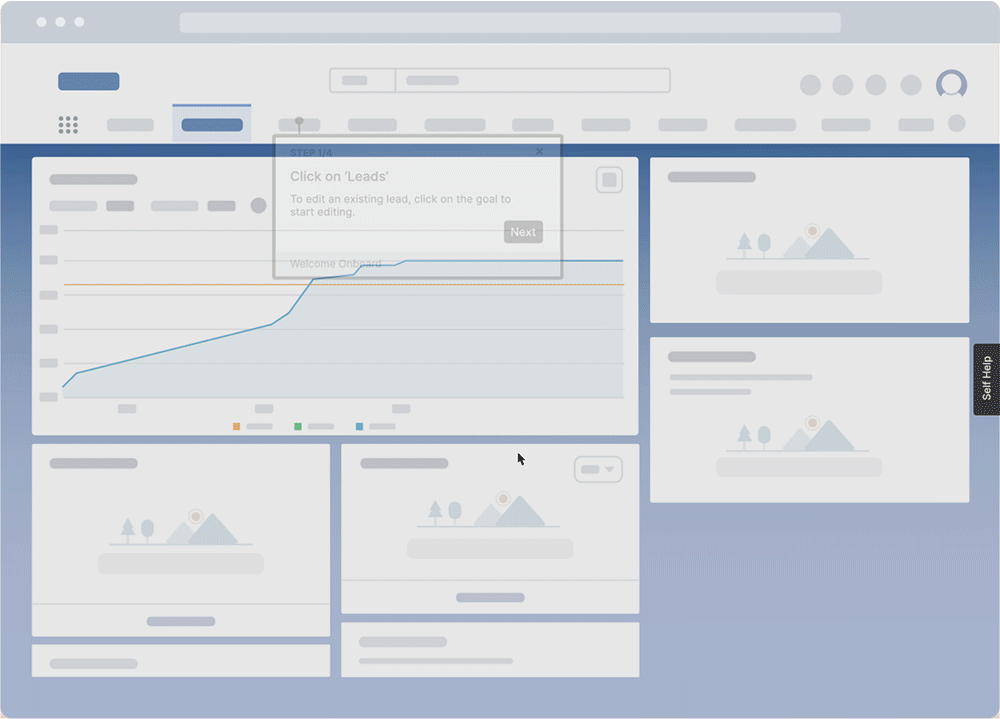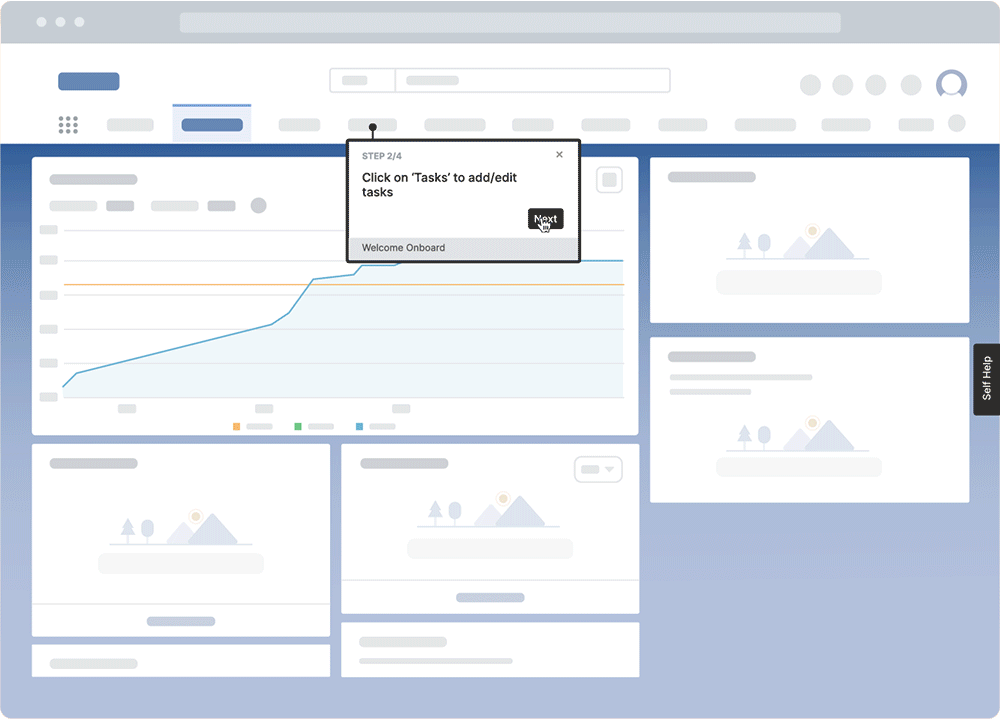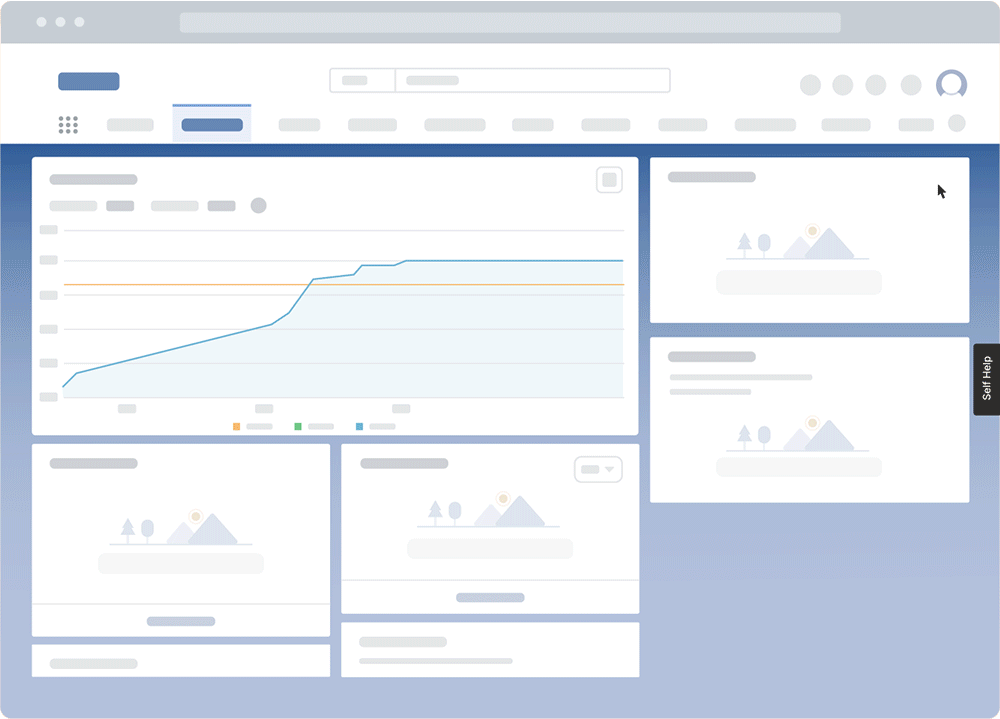
DAPs seemingly guide employees through software applications, offering contextual, role-based learning experiences and performance support and providing insight into how users engage with applications and in-app training. DAPs enable employees with user-friendly guidance that drives productivity and maximizes digital application ROI.

This “learning by doing” mentality fosters a culture of continuous learning and growth, all without sacrificing employee output.
Ready to learn more? Request a Whatfix demo today!
Thank you for subscribing!