Well-trained employees are an asset to an organization. Yet, organizations consider the cost of training employees as an additional overhead instead of an investment, especially in difficult times. The 2020 Training Industry Report suggests COVID-19 has led to declines in both the amount organizations are spending on employee training with a decrease of 1% to $82.5B, as well as an 18% decrease to $42.4B in training payroll expenses.
What Is the Average Cost of Training Employees?
On average, companies spent $1,111 per employee on training employees in 2020, compared to $1,286 per employee in 2019. Mid-size companies reported the least training expenses per employee of $581 in comparison to enterprise ($924) and small business ($1,678) companies.
Now money isn’t the only resource you spend on training employees. There is an accountability of the number of hours as well. While the cost per training employee went down, the number of hours of training per employee increased substantially from 42.1 hours to 55.4 hours annually.
Whether you hire a seasoned professional, are reskilling or and upskilling existing employee, or are training new employees – the cost of training is inevitable. It’s wise to manage the training budget more efficiently by understanding the factors that influence the cost of workplace training for your employees and how you can maximize your learning and development strategy’s ROI and work to reduce your training costs.
6 Factors that Influence Employee Training Cost
Though the above figures provide a useful insight into potential training costs, it’s an average training expense and the true cost of training differs for every business. Here is a list of the top 6 factors that influence the cost of employee training in the workplace.
1. Company Size
The size of any company decides its training expenditure. The cost of training is higher for smaller organizations compared to large organizations. Large organizations recruit multiple employees at once, reducing the training cost per employee. However, they spend more hours on training compared to smaller organizations.
2. Industry
Employee training cost differs according to industry. An industry-specific and extensive training program would be more expensive than a generic training program. Industries such as leisure and hospitality do not require extensive training programs; on-the-job training would suffice.
However, technical businesses need to provide more specialized forms of training. For example, Amazon commits millions to retrain over 100,000 non-technical workers into software engineering careers. Another example of an industry that must spend more on employee training programs is the healthcare industry.
3. Job Role
Training programs should be role-specific to increase their relevance and effectiveness. It helps employees perform better, leading to better business outcomes for the entire enterprise.
Opting for a personalized training program here will go a long way in increasing employee satisfaction. And of course training programs for more technical roles – such as a software engineer – will be more costly than training a new sales specialist.
4. Experience Level
Employee’s skillsets differ with experience levels. Organizations need to conduct an assessment for existing skills and learning needs before designing a training curriculum.
For example- An organization has a sales process where entry-level BDRs are responsible for qualifying potential customers, which are then followed up with and closed by more experienced, senior sales professionals. In this case, if you spend your training budget on the senior sales professionals to improve the number of closed deals, it would fail at the root cause of the problem. The organization would need to train the junior BDRs instead, leading to a better sales qualifying process that solves the root cause.
5. Training Method
Different methods of employee training have different costs and learning curves associated with them. You can choose from conventional instructor-led classroom training, on-the-job training, remote training, simulations, on-demand personalized eLearning, and many more. While instructor-led training became infeasible during the pandemic, eLearning became a popular medium for employee training because of its cost-effectiveness and convenience.
6. Hidden Costs
Apart from the obvious direct costs associated with employee training, you should watch out for the hidden costs as well. Potential hidden costs include:
- Administrative costs
- Premature employee turnover cost
- Costs incurred due to low employee productivity
- Cost of supplies
- Travel costs
- The cost incurred due to engaging supervisor’s productive hours
Is the Cost of Training Employees Worth It?
Now that we know the cost of employee training is high and intimidating, it is a valid question to ask whether organizations should bear the cost or not.
The following statistics will make the answer to this question evident:
- Gallup suggests 87% of millennials look at their jobs as a development opportunity making employee training imperative.
- Up to 20% of US employees quit within 45 days of their employment. This employee turnover can only be reduced through proper employee training and onboarding.
- According to an IBM study, 84% of employees in best-performing organizations are receiving the training they need, are 10% more productive, and have resulted in an annual savings of over $70,000 annually.
These statistics clearly show the importance of employee training in increasing employee satisfaction and reducing employee turnover. A well-designed employee training program makes your employees work smarter and reduces your operating costs.
Zig Ziglar rightly said that “The only thing worse than training employees and losing them is to not train them and keep them.”
How to Have High ROI on Training Investments in 2024
After setting a budget and organization need for employee training, you should work on an effective training strategy to minimize the training costs and maximize your returns.
The following tips will help you in creating a training strategy that drives ROI:
1. Improve the Learning Curve with Microlearning
Research suggests that within 24 hours, learners forget 70% of new information. With such high training costs involved, you should work on retention and reinforcement of information. Microlearning or bite-sized learning makes it easier to consume content and retain the information for a longer time.
2. Invest in a Digital Adoption Platform (DAP)
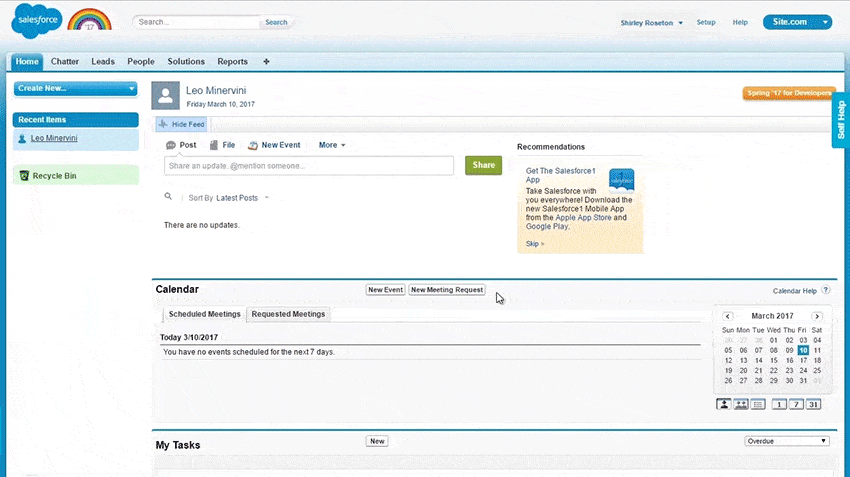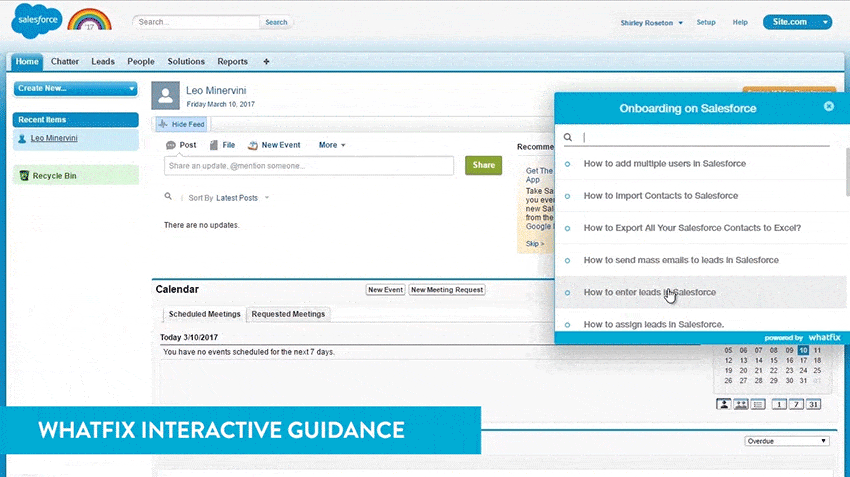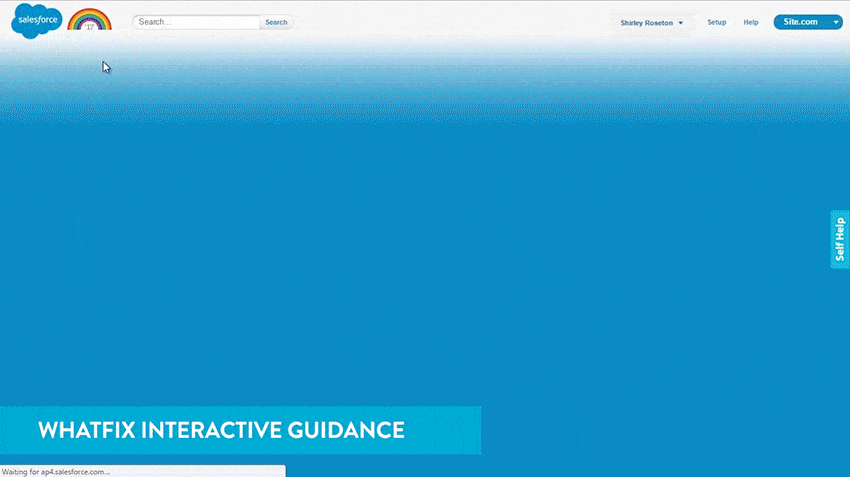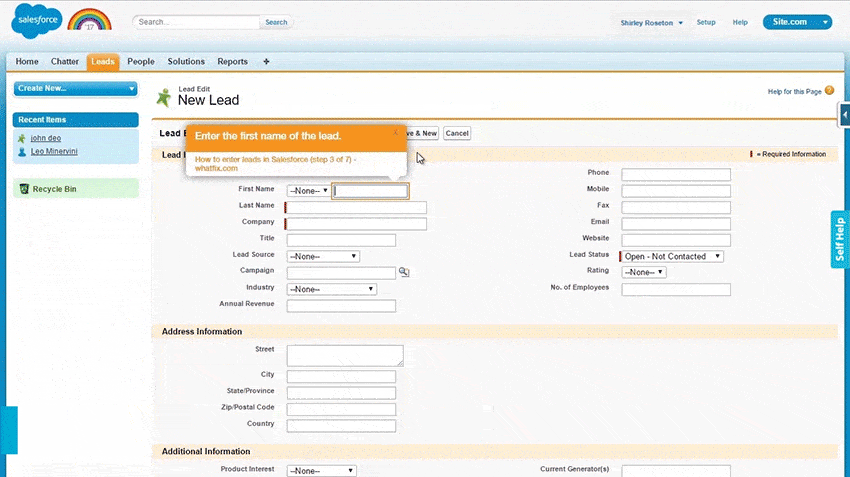
Digital adoption platforms such as Whatfix are an effective way to tackle the challenges of conventional training methods and effortlessly train your employees. Whatfix empowers your employees to learn in the flow of their work with interactive walkthroughs and multi-format content with self-help widgets.
It provides a personalized on-demand training experience, thereby making it more effective and allowing HR teams to measure training effectiveness.
Learn more about Whatfix for employee training now!
3. Optimize the Use of Your Training Budget
Several mid-size and enterprise companies spend 2-5% of their salary budgets on workplace training. To make the most of your training budget, it is crucial to hold employees accountable and monitor how these training initiatives translate into a measurable skill set.
You should set actionable training objectives and goals for employees and use training programs as part of employee annual performance reviews to address skills gaps.
4. Create Scalable Training & Onboarding Programs
Creating an individual training program for each employee isn’t feasible. You should create a scalable training and employee onboarding process to reduce the cost of training. You can also leverage the following employee onboarding checklist to guide employees through their initial phase at the workplace.
5. Take a Holistic Approach to Employee Training
An effective training strategy incorporates skill sets that employees want to learn. With changing business dynamics, requirements of skill sets change as well, and they might not necessarily be technical skills.
For instance, according to LinkedIn’s 2021 Workplace Learning Report, resilience and digital fluency are the power skills required in 2021. Therefore, a holistic employee training approach would go a long way in making the training programs more relevant and cost-effective.
With Whatfix, you can create scalable employee training flows built directly into your website or enterprise applications – allowing employees to learn in the flow of work. It provides segmented, contextual training and development self-help resources to employees in the moment of need, with analytics to measure and improve your training processes.
Get started with Whatfix for employee training today.
Request a demo to see how Whatfix empowers organizations to improve end-user adoption and provide on-demand customer support