Digital Transformation in Manufacturing in 2024 (+9 Examples)


Digital transformation is rapidly evolving the entire manufacturing industry. If CIOs of manufacturing companies don’t understand what’s best for their business and customers now and in the future, they’ll be left struggling with revenue, unproductive people, obsolete equipment, legacy software, and outdated processes.
To prepare for the future and remain relevant in their industry, manufacturing companies must invest in digital capabilities, software, and technologies to gain an edge in an already hypercompetitive market.
What Is Digital Transformation in Manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing is when an organization begins implementing new digital technologies to improve all aspects of the manufacturing process. This can be a wholesale approach or a piece-by-piece implementation where software applications and digitization are the biggest drivers.
Critical areas of digitalization in manufacturing are improving operations, providing better customer experiences, and big data. Examples include robotic process automation (RPA), mobile apps for frontline employee management, 3D printing, ERP systems, and automation of knowledge work.
Impact of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
The impact of digital transformation in manufacturing is wholesale and includes improvements in safety, quality, throughput, efficiency, revenue, and sustainability – all while reducing costs to remain competitive in the marketplace. The impacts are vast, and this transformation must happen to keep up with evolving customer needs and stiff competitors.
Here are a few major benefits of the digitalization of manufacturing companies:
- When you provide digital solutions that improve your safety, fewer workplace injuries and accidents occur
- When you improve your output quality, you are reducing rework of products, reducing warranty work, and increasing customer satisfaction.
- When you improve your process efficiency positively impacts employee productivity and your bottom line. A strong bottom line allows you to continue to innovate and drive sustainability in your market while increasing value for your company, shareholders, and customers.
Digital transformation has also led to real-time manufacturing data. These digital processes allow you to capture data instantaneously, corresponding to analysis for quicker real-time decisions by the organization. It’s not only for reactive responses but for predictive analytics to improve future processes and products. This normalizes preventative maintenance and failure approaches that directly affect all aspects of the business.
With digital transformation in manufacturing comes empowerment– empowerment to have a voice and do something about improving a process, hold yourself and others accountable to do better, and have a continuous improvement mindset in business.
Empowerment comes in many ways, but it is most powerful when aligned with the organization’s future vision and communicated effectively with the workforce.
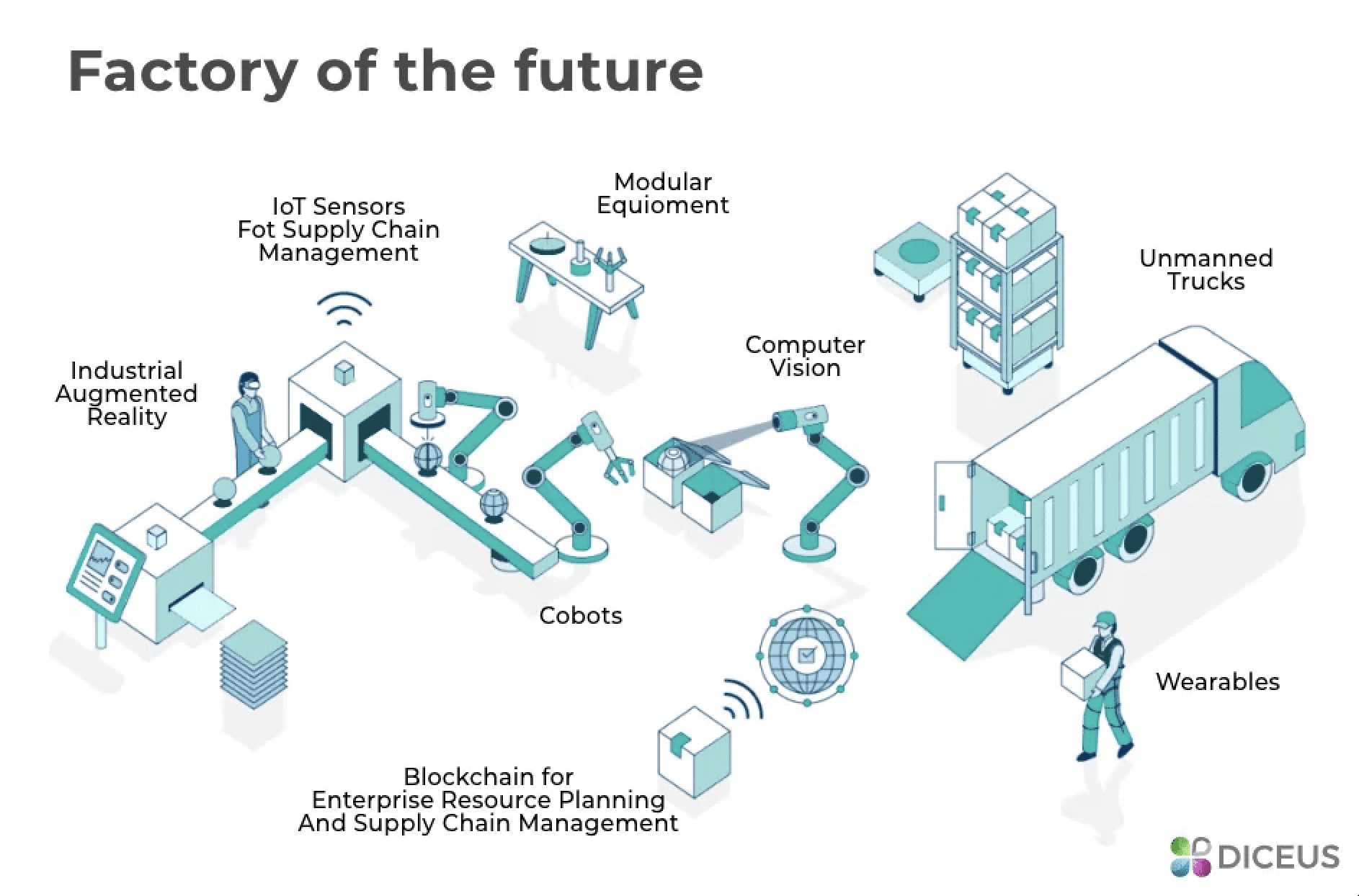
9 Examples of Manufacturing Digitalization in 2024
As all manufacturing processes and organizations are different and personalized, so are examples of what could be implemented and how it can be done. To help get manufacturing CIOs, CTOs, and other leaders started with digital transformation in the manufacturing industry, here are nine examples of manufacturing digitalization:
1. Industrial IoT sensors
These devices measure and monitor industrial processes. They can be deployed in the field, in manufacturing plants, or at other locations where there is a need to collect data about the performance of various equipment. It includes gas sensors that measure the amount of oxygen in a particular area, temperature sensors that monitor the temperature of an object or process, and pressure sensors that measure changes in air pressure around a device.
The most common applications for industrial Internet of Things (IoT) sensors include:
- Monitoring plant operations and equipment
- Monitoring energy consumption
- Managing inventory
- Tracking equipment maintenance
- Measuring environmental conditions such as humidity or temperature
2. Big data and analytics
Big data refers to the growing volume, velocity, and variety of data companies generate and collect. It has become an important part of business operations because it can measure performance and improve overall efficiency.
The use of big data allows manufacturers to identify trends in their business and take action on them. They can make informed decisions about product development, supply chain management, and other important aspects of running a manufacturing business.
3. AI, automation, and machine learning
AI-powered digital transformation is transforming manufacturing companies into smarter, streamlined, safer companies. One of the most exciting things about artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and machine learning is that they can make manufacturing companies more efficient by automating various tedious processes for workers. They also empower manufacturers to better predict trends and improve quality control, making products faster and reducing waste.

Manufacturing companies are already using these technologies in different ways. For example, one company may use AI technology to analyze data from its customers’ orders to make sure they’re getting what they want when they order something from them. Another company may use machine learning to find patterns in its customers’ data to predict what products they’ll be interested in buying next time.
4. Cloud-based ERP and other manufacturing software
Cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and other manufacturing software are applications that provide tools for managing business operations. A cloud-based ERP system can safely store your company’s data in the cloud, allowing you to access it anywhere. Implementing a new ERP makes it easier for employees to collaborate on projects or access information when they’re not at their desks. You can also use cloud-based ERP software to manage your inventory, production, customer relationships, and more.
Manufacturers are increasingly turning to cloud-based ERP systems purpose-built for manufacturing companies to streamline their operations. These systems enable manufacturers to access the same tools they use in their offices, allowing them to spend less time on paperwork and more time focusing on what they do best: creating products.
With these new platforms, manufacturers can track their inventory in real-time, so they never have to worry about running out of stock. They also make it easier for manufacturers to communicate with customers and partners, which means more sales and fewer headaches for everyone involved.
5. Smart manufacturing
Smart manufacturing is a term used to describe the use of digital technology and automation to communicate with other devices or systems and gather data about the system’s operation.
Smart manufacturing can be applied to all aspects of manufacturing, including production management, quality control, and supply chain management.
The goal of smart manufacturing is to take advantage of new technologies to make processes more efficient and productive.
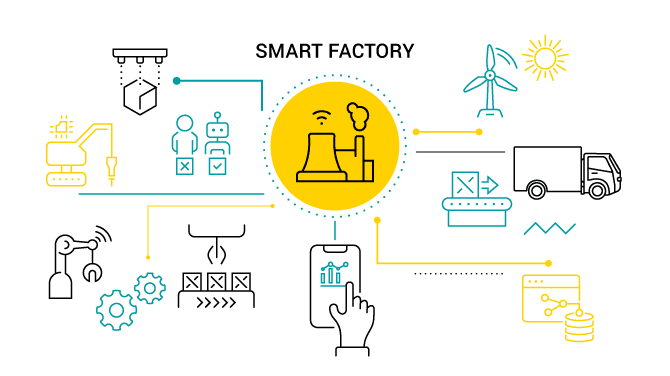
The key benefits of smart manufacturing include:
- Improved quality control and production scheduling
- Better inventory planning
- Faster problem resolution
- Reduced overall costs
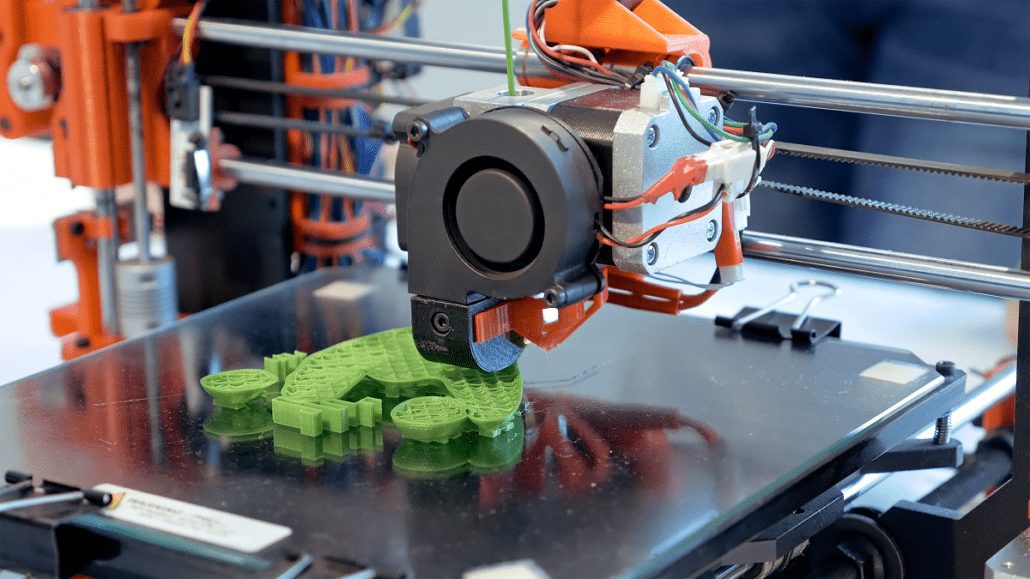
6. 3D printing
3D printing is one of the most transformative manufacturing technologies in recent years, and other industries have already used it to innovate new products.
3D printing is a process that creates objects from digital data. It uses lasers to lay down layers of material, which harden to create the object. The technology can be used to make entire objects or the parts that make them up.
7. Online marketplaces for buying and exchanging CNC machinery, parts, and tools
Manufactures require highly-customized CNC machinery to keep operations efficient and live. Inevitably companies will need to replace old machines, find replacement parts, and purchasing hard-to-find tools. This has led to a boom in highly-specialized online marketplaces for finding, replacing, and exchanging CNC machinery, parts, and tools, allowing machinists and manufacturing companies the freedom to browse, compare, find, and purchase CNC-related items through online ecommerce stores.
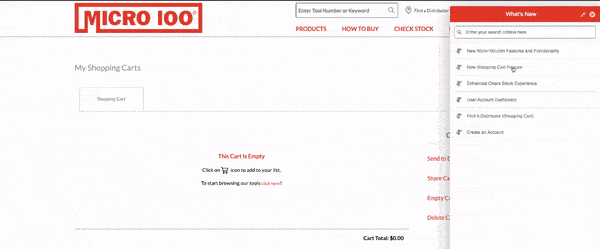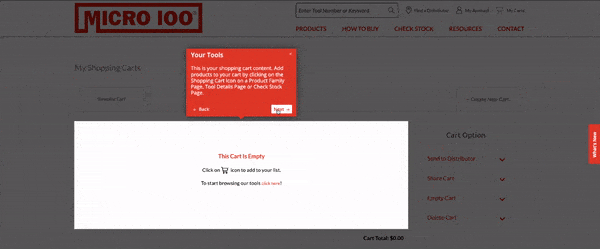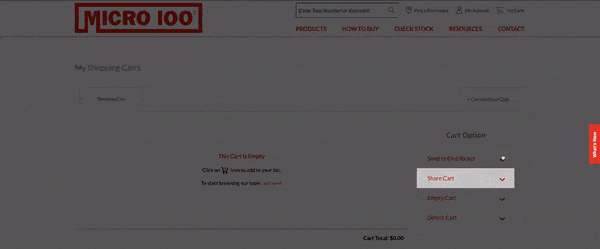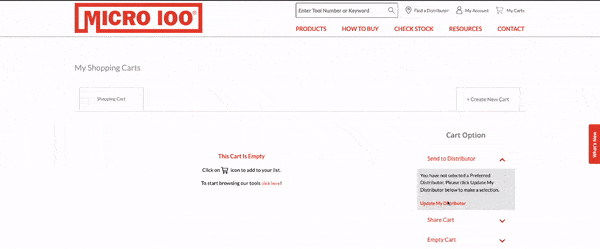
One such online marketplace is Micro100. Online marketplaces present entirely new challenges for companies, which must now manage an online product, track and improve user experience, release new buying portal features, etc. Micro100 began to optimize its website buying journey and shopping experience with new features and product updates that proved to be winners in testing.
However, when it launched these features, its less tech-savvy buyers experienced heavy friction in the new shopping experience, leading to high shopping cart abandonment rates, website bounces, and IT support tickets.
Micro100 partnered with Whatfix to create in-app tutorials to enable its customers with guided website experiences to adopt new features, reduce shopping cart abandonment, and sell more products.
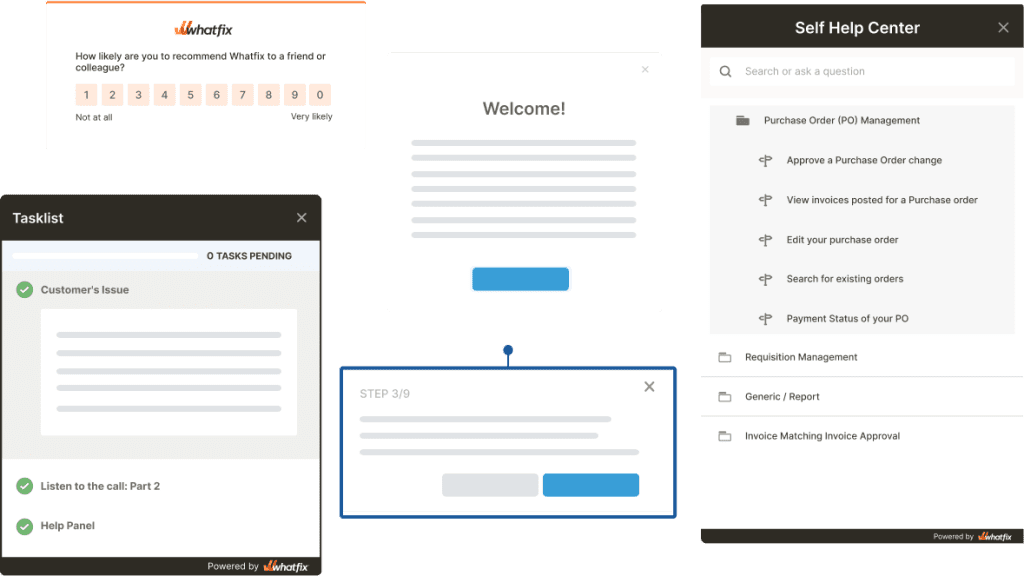
With Whatfix, Micro100 created an in-app resource center (Self Help), including FAQs, how to set up a new account, and all new features and product updates. Each entry triggered an in-app guided Flow when a user clicked on it, helping users learn in their workflow and experience their “aha!” moment. This ultimately drives new feature adoption for new marketplace updates and empowers Micro100 to create sticky, user-friendly online buying experiences that enable customers to use its online CNC store.
8. Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a methodology that helps manufacturers monitor equipment and machinery for signs of wear. It can also help predict when parts need to be replaced or if something needs to be fixed before it breaks down.
In this way, it is similar to preventive maintenance in that it prevents problems from occurring in the first place. However, predictive maintenance on work order software also provides insight that can help reduce downtime and increase operational efficiency.
Predictive maintenance systems are used by various industries, including automotive, oil and gas, building construction and maintenance, pharmaceuticals, and more.
Predictive maintenance systems constantly monitor the health of your equipment and make adjustments as needed. This means that even while you’re not looking at your equipment, it’s already working to keep it running at its best.
This type of system also has the added benefit of helping save money on repairs and maintenance costs because it allows you to avoid problems before they happen.
9. Augmented and virtual reality
Augmented and virtual reality are two terms often used interchangeably, but they are quite different.
- Augmented reality is when a user’s surroundings are enhanced by computer-generated information. You can see this in the graphic below.
- Virtual reality is when the user is completely immersed in a digital environment.

In manufacturing, both technologies have been used to help businesses improve their processes and increase efficiency. For example, a company may use augmented reality to display instructions for assembling an item on its employees’ screens or create a simulation of their production line in a virtual space so workers can see what the finished product would look like before they begin production.
4 Digital Transformation Challenges in Manufacturing
Digital transformation in manufacturing is evolving, and every evolution has unique challenges. Manufacturers today need to keep up with the rapid pace of change while also ensuring they facilitate business growth.
The following will highlight key digital transformation challenges manufacturers must overcome when implementing new digital technologies.
1. Investing in the right technology
In the manufacturing industry, one of the biggest challenges is investing in the right technology. The ability to innovate and stay ahead of your competition is essential, but it’s not enough. The success of a manufacturing company depends on having the right tools for the job, and those tools need to be adaptable and scalable so they can grow with you as your business grows.
2. Managing change effectively
The challenge of managing change effectively is one of the biggest hurdles for companies that want to implement digital transformation in manufacturing.
As companies move toward automation, it’s essential to consider how their processes will evolve with the technology. This can be difficult given that many traditional manufacturing processes are built around human interaction and may not be easily or quickly adaptable.
However, there is hope for those willing to take a fresh look at their current systems, and hiring a digital transformation consultant can make things easier. While change is inevitable, companies must take time to understand exactly what they need from their new systems before implementing them.
3. Onboarding, training, and reskilling employees
Another challenge with digital transformation in manufacturing that requires significant planning is creating an implementation plan that helps organizations onboard and train employees on how to use these new tools. This may also fall under an organization’s digital adoption strategy for new technologies.
Many new technologies require reskilling on new competencies and processes, so getting everyone on board is not always easy and is a difficult employee training challenge all organizations implementing new tech face.
For example, if you’re using a new software program or a robotic machine, it might require specialized training to be sure all workers are familiar with their work.
And while some companies have programs that help with this process, others don’t—which means it may take longer to catch up with other companies who have streamlined their operations.
Onboarding and training manufacturing employees on these new systems empower team members to find full value in these new technologies. This drives digital adoption and allows manufacturing companies to maximize their technology ROI.
4. Scaling organization-wide to avoid silos
In the manufacturing environment, silos are a major challenge. Because of this, digital transformation often fails as it cannot scale from the individual to the organization-wide level.
The reason for this is simple: organizations have different business objectives, and these objectives need to be communicated and understood by all employees within an organization.
If an organization lacks a culture where people feel free to share their ideas, or if there are employees who do not want to share their ideas, then digital transformation will fail because no one will be able to work together effectively as a team.
To find true ROI of your software and technology investments, organizations should implement a digital adoption platform like Whatfix. Whatfix empowers employees and customers to get the most of new applications and digital processes by providing in-app guidance, reinforcement training, in on-demand support – all directly embedded inside your digital applications and tools.
Whatfix not only provides the no-code tools to create this in-app content, but provides user analytics for organizations to understand how their in-app content is being consumed, what features or processes are causing issues with employees, what processes need additional support and training, and to drive overall user adoption.
Thank you for subscribing!



